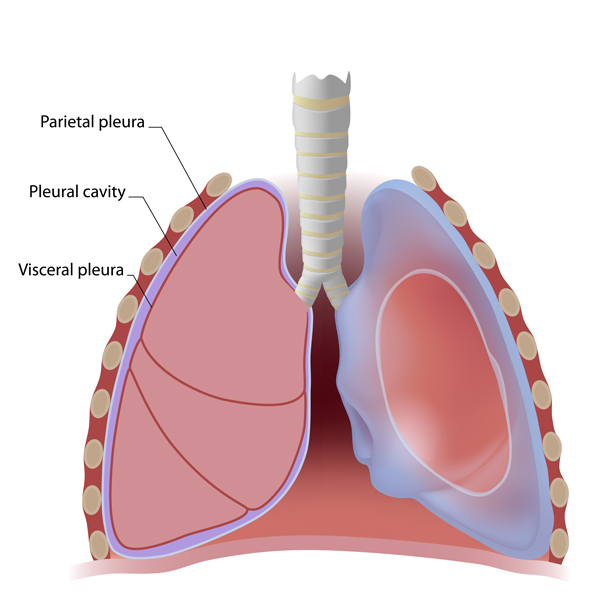
The pleural space is the small gap between the lung and inside of the chest wall, which usually contains a tiny amount of fluid. Problems with the pleural space may include entry of air (causing a collapsed lung or pneumothorax), a build-up of fluid termed a pleural effusion, or some tumours.
The most common procedure performed in the pleural space is a pleurodesis, where talcum powder is introduced into the space to cause the lung to stick to the chest wall and obliterate the pleural space on that side. This may be done for either a pneumothorax or for an effusion, and may be combined with a biopsy of the pleural lining or removal of a damaged area of lung.
Mesothelioma is a cancer of the pleura caused by exposure to asbestos, sometimes many years earlier. By the time it is diagnosed, mesothelioma is rarely curable, but your surgeon may recommend a procedure to confirm the diagnosis with a biopsy and prevent development of an effusion by means of a pleurodesis. Most patients diagnosed with mesothelioma cannot be cured but may be offered palliative treatment with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. Because it is always caused by exposure to asbestos, patients and their families may be able to make a claim for financial compensation.